 |
| Great location and transport links |
|
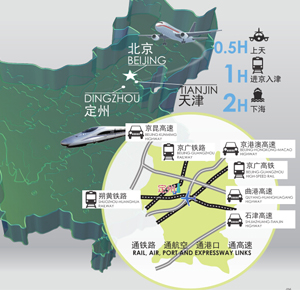
The city sits in the heartland of the Beijing-Tianjin-Shijiazhuang triangle. One high-speed railway, two regular railways and three expressways runs through the city, making Dingzhou just one hour away from Beijing and Tianjin, 30 minutes from the airport and two hours from sea ports. The city is an important transport hub connecting Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei and Shanxi.
Rail, air, port and expressway links.
Dingzhou Rail Station has a passenger capacity of 1.8 million per year and freight capacity over one million tons.
The city has teamed up with Beijing Rail Corporation to build a modern logistics base with an annual throughput in excess of 100 million tons.
|
|
 |
| Long history and rich cultural heritage |
|
The city was built over 2,600 years ago and was named the capital of the Zhongshan kingdom for three times during the Warring States period and the Han Dynasty, and had been the capital of the region throughout history. After the establishment of the People's Republic, a prefectural office was set up. The city has been a regional economic, political, cultural and military center since its history began.
The city is home to generations of dignitaries.
(Illustration showing Liu Yuxi, Han Qi, Su Shi, Yan Yangchu, Wang Senran, Zhang Hanhui et al.).
|
|
 |
| Long history and rich cultural heritage |
|
One of the Five Kilns of China and the birthplace of Ding porcelain, Dingzhou Kesi (silk tapestry weaving), Gold-threaded Jade Suit, and Zhongshan Song Lao wine. Dingzhou Yanko dance and Dingzhou Chui (blowing) song have been included in the National Intangible Cultural Heritage List. The city is the chief site of origin and inheritance of the "Zhongshan Culture"—one of the three main historic cultures of Hebei.
|
|
 |
| Solid industrial foundations |
|
Key green thermal power, equipment manufacturing and high-tech industrial bases of the province have been established in Dingzhou. The city also houses the largest dairy and animal farming equipment production base in Asia and is a key production area of China's grain, edible oil, meat, vegetables, flowers and nursery stock.
|
|
 |
| Well-developed estate functions |
|
The estate boasts its huge scale in the province and possesses 1 national and 4 provincial-level campuses. The National Agricultural Technology Estate and High-tech Development Area have been assigned as platforms to accommodate the diverted urban functions and relocated industries from Beijing and Tianjin.
|
| Abundant land resources |
|
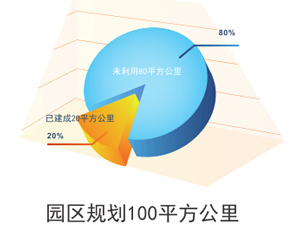
The city has a planned urban area of 100 sq. km. and over 100 sq. km. have been planned for the city's development area. 3,000 hectares of unutilized land have been gathered in reserve, ready for ongoing projects at any time.
|
|
 |
| Powerful intellectual support |
|
Wuhan University, Tianjin University, Bohai University, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, among other academic institutions, have set up research institutes in Dingzhou. The city is also home to two universities, a national Occupational Education Center, a century-old school renowned nationally. The city's occupational education ranks among the top nationwide and boasts a highly competent talent pool.
|
|